|
|
 List navigation
List navigation
|
| Home page | Home page of the taxonomy |
| Top level |
organum  Short Extended Short Extended
|
| Level 2 |
organum membrana  Short Extended Short Extended
|
| Subsidiary language with Latin |
|
| Non Latin primary language |
 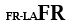 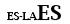
|
 Ancestors
Ancestors
|
| Help on colors |
|
| FMA:62955 | |
| FMA:61775 | |
| FMA:67165 | |
| FMA:305751 | |
| FMA:67135 | |
| FMA:67498 | |
| FMA:55670 | |
| FMA:55665 | |
| FMA:7145 |
 organum membrana organum membrana 
|
 Taxonomic list
Taxonomic list
|
| FMAID | TA | UID | Pair |
Short official Latin term
|
Short French equivalent
|
||
| 7145 |

|
10406 |
organum membrana

|
organe membrane

|
|||
| 9592 |

|
5091 | part |
pachymeninx

|
pachyméninge

|
||
| 59328 |

|
7032 | part |

|
septum orbitale

|
cloison orbitaire

|
|
| 302986 |

|
13877 |
membrana skeletalis

|
membrane squelettique

|
|||
| 24012 |

|
17386 |
membrana atlantooccipitalis

|
membrane atlantooccipitale

|
|||
| 25005 |

|
1368 | part |
membrana atlantooccipitalis anterior articulationis atlantooccipitalis

|
membrane atlantooccipitale antérieure d'la articulation atlantooccipitale

|
||
| 25006 |

|
1370 | part |
membrana atlantooccipitalis posterior

|
membrane atlantooccipitale postérieure

|
||
| 76873 |

|
1429 | part |
membrana sterni
|
membrane sternale

|
||

|
17424 | part |

|
membrana sternalis costae secundae

|
membrane sternale de la deuxième côte

|
||

|
17425 | part |

|
membrana sternalis costae tertiae

|
membrane sternale de la troisième côte

|
||

|
17426 | part |

|
membrana sternalis costae quartae

|
membrane sternale de la quatrième côte

|
||

|
17427 | part |

|
membrana sternalis costae quintae

|
membrane sternale de la cinquième côte

|
||

|
17428 | part |

|
membrana sternalis costae sextae

|
membrane sternale de la sixième côte

|
||

|
17429 | part |

|
membrana sternalis costae septimae

|
membrane sternale de la septième côte

|
||
| 54839 |

|
17463 |
membrana interossea

|
membrane interosseuse

|
|||
| 35187 |

|
1529 | part |

|
membrana interossea cruris

|
membrane interosseuse du pédoncule

|
|
| 23706 |

|
1455 | part |

|
membrana interossea antebrachii

|
membrane interosseuse de l'avant-bras

|
|
| 25709 |

|
1512 | part |

|
membrana obturatoria

|
membrane obturatrice

|
|
| 34836 |

|
18022 |
capsula articularis

|
capsule articulaire

|
|||
| 55106 |

|
2848 | part |
capsula articularis cricothyroidea

|
capsule articulaire cricothyroïdienne

|
||
| 55305 |

|
2866 | part |

|
capsula articularis cricoarytenoidea

|
capsule articulaire cricoaryténoïdienne

|
|
| 9595 |

|
7153 | part |

|
membrana tympanica

|
membrane tympanique

|
|
| 56958 |

|
7180 | part |

|
membrana tympani secundaria
|
membrane tympanique secondaire

|
|
| 9586 |

|
3716 | part |
pericardium fibrosum

|
péricarde fibreux

|
||
| 77436 |

|
3718↓ | part |
membrana bronchopericardiaca

|
membrane bronchopéricardiaque

|
||
| 60959 |

|
7220 | part |

|
membrana stapedia

|
membrane de l'étrier
|
|
| 59086 |

|
17871 |
tarsus palpebrae

|
tarse de la paupière

|
|||
| 59087 |

|
7067 | part |

|
tarsus superior

|
tarse supérieur

|
|
| 59088 |

|
7068 | part |

|
tarsus inferior

|
tarse inférieur

|
|

|
8215↓ | part |

|
diaphragma epitympanicum

|
diaphragme épitympanique

|
||
| 55132 |

|
2836 | part |

|
membrana thyrohyoidea

|
membrane thyrohyoïdienne

|
|
| 55239 |

|
18029 |
membrana fibroelastica laryngis

|
membrane fibroélastique du larynx

|
|||
| 55247 |

|
2914 | part |

|
membrana quadrangularis laryngis

|
membrane quadrangulaire du larynx

|
|
| 55239 |

|
2913 | part |

|
membrana fibroelastica laryngis

|
membrane fibroélastique du larynx

|
|

|
34 items
|
|
|||||

|
76 entities
|
|
 Scientific notes
Scientific notes
|
| UID |
Libelle of note
|
| 3718 |
Membrana bronchopericardiaca A connective tissue membrane consisting mainly of collagenous fibres that extends from the anterior surface of the tracheal bifurcation via the dorsal wall of the pericardium to the diaphragm. Three fibre directions can be discerned. Vertical fibres run in the direction just mentioned. Transverse fibres run from the pericardium into the lung where they join the adventitia of the large pulmonary veins. Oblique fibres extend from the two main bronchi diagonally over the pericardium into the opposite pulmonal ligaments. The membrane is the borderline between the middle and the posterior mediastinum, together with the tracheal bifurcation. Its function is to stabilize the tracheal bifurcation and that of the main bronchi, in relation to the dorsal aspect of the pericardium and the pulmonary hilus, during movements relating to respiration, the larynx, and the head. Benninghoff Anatomie. 1994. Edited by Drenckhahn D. and Zenker W. Vol. 1. p. 557. München-Wien-Baltimore: Urban & Schwarzenberg. Rauber/Kopsch. 1987. Anatomie des Menschen. Edited by Leonhardt H. Vol. 2, p. 159. “Innere Organe." Stuttgart, New York: Georg Thieme.
|
| 8215 |
The diaphragma epitympanicum (epitympanic diaphragm) separates the epitympanum from the mesotympanum. The diaphragm is formed by the lateral incudomallear and mallear folds laterally, and the tensor tympani fold anteriorly. The epitympanum and the mesotympanum communicate through two openings in the diaphragm, known as the isthmus anterior and isthmus posterior.
|
 Signature
Signature
|
| Type of list | T2 |
| List Unit Identifier | 10406 |
| Subtotals | subchildren 0 subunits 0 |
| Proper children | 75 |
| Number of children | 75 (validated) |
| Proper units | 34 |
| Number of units | 34 (validated) |
| Signature | 311 (validated since 31.12.2024) |
| Date: 23.08.2025 |